RS-1 (Rapid setting Emulsion) for Tack coat.
Rapid setting emulsion is a specialized type of bitumen emulsion designed for tack coat applications. It’s characterized by its quick-setting properties, allowing for rapid bonding between layers of asphalt. This rapid setting is achieved through a chemical reaction that occurs when the emulsion comes into contact with the aggregate. Tack coat applications, such as ensuring adhesion between new and existing asphalt layers, require a product that sets quickly to minimize the risk of slippage or unevenness in the finished surface. The rapid setting emulsion’s efficiency in this regard makes it a popular choice in road construction and maintenance projects.

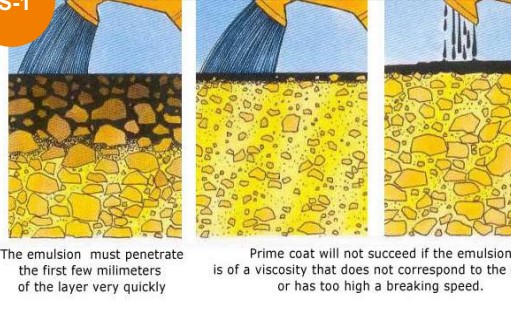
CSS-1(Water based Slow setting Emulsion) for Prime Coat
Water-based slow-setting emulsion is a specialized type of bitumen emulsion designed for prime coat applications. Unlike rapid-setting emulsions, this product is formulated to set more slowly, allowing for better penetration into the base material. This slower setting time is particularly beneficial for prime coat applications, as it ensures that the emulsion can effectively bond with the underlying surface, providing a strong foundation for subsequent layers of asphalt. The water-based nature of this emulsion offers advantages such as reduced environmental impact and improved handling properties.

SS-1 (Oil based Slow Setting Emulsion) for Prime Coat
Oil-based slow-setting emulsion is a specialized type of bitumen emulsion designed for prime coat applications. Unlike water-based emulsions, this product is formulated using oil as a carrier, which can provide certain advantages in specific conditions. For instance, oil-based emulsions may exhibit better resistance to moisture and certain environmental factors. The slower setting time of this emulsion allows for deeper penetration into the base material, ensuring strong adhesion between the prime coat and subsequent layers of asphalt. However, it’s important to note that oil-based emulsions may have different environmental implications compared to water-based options.
CME Cold Mix Emulsion for Construction of Rural Roads.
Cold mix emulsion is a specialized type of bitumen emulsion designed for the construction of rural roads. It offers several advantages over traditional hot mix asphalt, including lower energy consumption, reduced emissions, and easier handling. Cold mix emulsions can be mixed with aggregate at ambient temperatures, eliminating the need for costly heating equipment. This makes them particularly suitable for rural areas where infrastructure and resources may be limited. The cold mix process also allows for faster construction times and reduced disruption to local communities.
CQS (Cationic Quick Setting Emulsion) for Microsurfacing Layer.
Cationic quick-setting emulsion is a specialized type of bitumen emulsion designed for microsurfacing layer applications. This type of emulsion is characterized by its positively charged particles (cations), which allow for better adhesion to the existing road surface. The quick-setting properties of this emulsion ensure rapid bonding and minimal disruption to traffic flow during construction. Microsurfacing layers, which consist of a thin layer of asphalt, aggregate, and polymer, are often used to improve road surfaces, enhance skid resistance, and extend their lifespan. Cationic quick-setting emulsion is a popular choice for this application due to its efficient performance and ability to provide a durable and long-lasting surface.
PME for Fog Seal and small maintenance using Slurry Seal application.
Polymer modified emulsion (PME) is a specialized type of bitumen emulsion that incorporates polymeric additives to enhance its performance properties. It’s commonly used in fog seal and slurry seal applications for small maintenance projects. Fog seals involve applying a thin layer of PME to the road surface, followed by a light sprinkling of aggregate. This process helps to rejuvenate the existing asphalt, improve its skid resistance, and protect it from weathering. Slurry seals are similar but involve a thicker application of PME mixed with aggregate, providing a more substantial layer of protection. PME’s enhanced properties, such as improved adhesion, durability, and resistance to cracking, make it an ideal choice for these types of maintenance applications.
